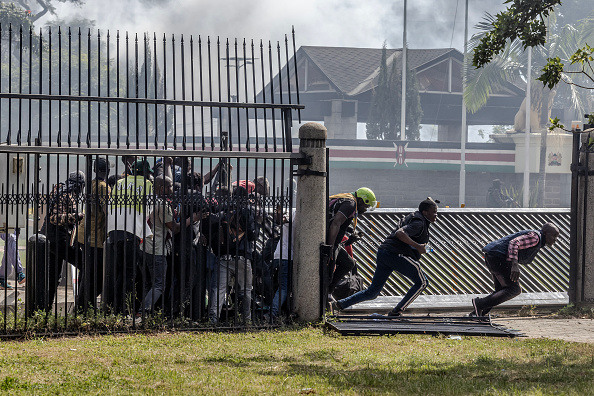In Global Guardian's monthly Risk Barometer, our Intelligence Team highlights current global hotspots with the potential to impact your business operations and travel. Read below for analysis on the threats we are closely monitoring this month and click here to subscribe for regular intelligence updates.
Russia Escalates Sabotage Campaign in the West
A Russian espionage and sabotage campaign in Europe and North America has intensified over the past several months. As Ukraine’s allies augment the quality and quantity of their support for Kyiv, Moscow appears poised to increase the use of “active measures” against Western targets, including operations ranging from cyberattacks and disinformation to sabotage and targeted violence. Private companies — particularly those linked to the Ukrainian war effort — are at growing risk from Russian sabotage and disruptive activities.
In the past month, several conspicuous fires have broken out at factories in the West producing military supplies for Ukraine. On 03 May, a major chemical fire was reported at a Berlin factory owned by German arms company Diehl Group, which manufactures Ukraine-bound air-to-air missiles, leading to a brief evacuation of the nearby area. On 17 April, a BAE Systems factory in southern Wales that produces 155mm artillery shells (a critical commodity on the front in Ukraine) suffered a major explosion. Similarly, on 15 April, an army ammunition plant that manufactures the same shells in Scranton, Pennsylvania, caught fire. Two men in Britain were also detained last month for setting fire to a warehouse containing aid destined for Ukraine. While evidence linking Russian agents to these incidents has thus far emerged in only one case, past instances of such sabotage have been attributed to Russian military intelligence.
Russia is also disrupting logistics in Ukraine-allied countries where it can. On 30 April, Finnair announced a month-long suspension of flights to the Estonian city of Tartu due to Russian GPS jamming in the Baltic. In Sweden, security services are investigating a spate of freight derailments as possible acts of Russian sabotage. In Czechia, rail signaling systems have come under what is believed to be Russian attacks. Additionally, on 17 April, two German-Russian dual nationals were arrested for scouting targets — including U.S. military bases — for Russian sabotage.
- Global Guardian recommends that companies involved in military supply chains conduct robust security audits and increase physical and cyber security measures.
- We recommend a heightened security posture for firms with assets or personnel in Eastern Europe, particularly the Baltics and Poland.
Previous Russian-Attributed Sabotage Incidents
- 25 June 2023: A large fire is reported at the EMKO arms depot in Karnobat, Bulgaria.
- 27 April 2015: EMKO’s owner, Emilian Gebrev, and his son, are poisoned in an assassination attempt by GRU team 29155.
- 03 December 2015: A series of explosions linked to GRU unit 29155 take place at Warehouse No. 20 near Vrbetice, Czechia.
- 16 October 2014: Explosion at Warehouse No. 16 linked to GRU unit 29155 near Vlachovice, Czechia.
Context
These incidents highlight a clear pattern: Russia’s clandestine efforts are taking on a distinctly material objective, crossing the line that divides routine intelligence gathering from what Russian intelligence calls “active measures.” Russia’s all-of-society approach to its own prosecution of the war in Ukraine is mirrored in attacks on “all of Western society,” including, primarily, those companies that provide aid in any form to Ukraine. Incidents of this kind will likely increase in frequency as Russia exploits the gap between the importance of and security posture of private enterprises supporting the war effort in the West.
Analysis
Russia’s overarching strategic objective for the medium term is to convince the Ukrainian people and Western policymakers that a Russian victory is inevitable. While the path to a Ukrainian victory is hazy, if Russia is able to demoralize Ukraine and hamstring Western aid, Moscow has a clear route to securing a favorable bargaining position in future peace talks.
Russia’s aggressive actions in the West are also, in part, a response to asymmetric Ukrainian successes within Russia itself. Ukrainian operatives successfully carried out dozens of acts of sabotage inside Russia, including the destruction of a key Siberian rail tunnel last winter, the bombing of a munitions factory near Moscow, and an explosion at an intercontinental ballistic missile plant.
While Russia is doing everything it can to hit infrastructure in Ukraine with its drone and missile salvos, most of Ukraine’s munition production is done in Western countries where a drone or missile attack would be too provocative — potentially leading to a direct confrontation with NATO. Unable to attack Western manufacturing overtly and unwilling to let support to Ukraine flow unimpeded, Russia has chosen the middle path of hybrid war.
Looking Forward
We expect increased attacks on critical infrastructure and defense manufacturing in Ukraine’s principal allies, including the Baltic states, Poland, France, the UK, Germany, and the United States. Water management systems and hospitals — which often lack protections against sophisticated cyber actors — are particularly at risk. The likelihood of a Russian cyberattack on the upcoming Olympic Games is also very high. A Russian attack — similar to the one carried out during the 2018 Olympics — is made more likely by Macron’s recent support for putting European troops in Ukraine.
Key Takeaways Companies involved in defense-related sectors are now considered “fair game” for Russia. While Russia cannot militarily strike an American or European production facility the way it targets Ukrainian factories, Moscow has options for disruption or harming production. These options include cyberattacks, information campaigns, sabotage, and arson. |
Anti-Israel Campaign Intensifies, Presaging More Unrest
Anti-Israel protests have spread from campuses in the United States (U.S.) to Canada, Europe, Australia, and Mexico in the largest student-led protest movement since the Vietnam War. In many instances, protests have been met by heavy-handed policing or counter protesters. Despite the coming end of the academic year, the protests are unlikely to dissipate in the near term. Unrest related to the war in the Middle East will likely continue to disrupt business and travel into the near term.
On 17 April, Columbia University’s president, Minouche Shafik, was called before a congressional hearing concerning antisemitism on U.S. campuses. Shafik, unlike previous university heads from Harvard, Yale, and MIT, took a hard line against antisemitic rhetoric at anti-Zionist student protests. In response, anti-Israeli protesters formed an encampment on Columbia’s grounds. On 18 April the encampment was forcefully cleared by NYPD at the university’s request, resulting in more than 100 arrests. Over the following weeks, protesters set up encampments modeled on Columbia’s at dozens of universities. As a result, commencements at Columbia and USC have been canceled. At least 2,800 protesters have been arrested or detained since Columbia’s encampment was cleared across roughly 50 campus protests.
- Global Guardian recommends avoiding university campuses and the surrounding areas if possible.
- We expect more commencement ceremonies to be canceled.
Context
The October 7 Hamas Pogrom in Israel and the subsequent Israeli invasion of Gaza set off a wave of global civil unrest. More than eighty countries have seen anti-Israel protests, including major demonstrations in the U.S., France, Germany, the Netherlands, the UK, and Canada.
In the U.S., the protests quickly became polarized along generational lines. Young Americans are overwhelmingly critical of Israel’s campaign in Gaza, while older generations — which include both President Biden and most Congress members — have remained largely supportive of Israel’s right to self-defense.
Starting in October of 2023, students began protesting Israel’s response to the Hamas attack. Initially, university faculty were supportive of the protesters — even going so far as to condone a minority of demonstrators who had engaged in legitimately antisemitic and pro-Hamas rhetoric. This led to the resignation of multiple university presidents, including Harvard’s.
Timeline
- 15 April: As part of a global “economic blockade to free Palestine,” demonstrators block traffic on Interstate 880 in Oakland, the Golden Gate Bridge in San Francisco Bay Area, Interstate 190 leading into O’Hare International Airport in Chicago, the Brooklyn Bridge in New York, Interstate 5 in Eugene, Oregon, the State Route 518 off-ramp to Seattle Tacoma Airport, and Interstate 76 and I-95 in Philadelphia.
- 17 April: Columbia University President addresses Congress; campus encampment begins.
- 18 April: Columbia encampment is partially cleared by NYPD with over 100 people detained.
- 21-22 April: NYU, Yale, University of Michigan, MIT, Emerson, and Tufts students set up encampments. Dozens of protesters are arrested at NYU and Yale.
- 30 April: Columbia students occupy Hamilton Hall and UCLA’s protest is attacked by counterdemonstrators using pepper spray and fireworks for four hours before police intervene and clear the encampment.
- 02-03 May: Students in Paris occupy one of Science Po’s buildings; French police forcefully remove protesters at Science Po.
- 06 - 07 May: Columbia University cancels graduation ceremony. Police and protesters clash in and around the University of Amsterdam, Netherlands.
Analysis
The anti-Israel movement has modeled itself in large part on the anti-Vietnam War protest movement, which saw large-scale student participation, and a violent crackdown by security services, including, famously, the killing of four students at Kent State University in Ohio. The U.S.’s military support for Israel and the crack down on anti-Israeli demonstrations have deeply energized a youth population whose median position on Israel was already highly negative. Added to this are the youth’s overwhelmingly negative perception of the police, which is borne in part from the legacy of the 2020 BLM protest movement.
The encampment tactics were designed to force university action through disruption. But under the threat of congressional pressure, the action that university leaders were able to take — clearing encampments — did not alleviate student-led protests but rather inflamed them.
Looking Forward
While many schools are undergoing their final exams now, the anti-Israel protest movement is not likely to dissipate with the arrival of summer break. As foreshadowed at the Met Gala, White House Correspondents Dinner, and elsewhere, anti-Israeli protesters will attach themselves to any event that draws significant media attention or has any meaningful connection to Israel, Israeli economic interests, or the Biden administration.
This summer, both President Biden and former President Donald Trump are set to attend their respective party's nominating conventions, events that are expected to attract political energy and attention. Additionally, this period marks the fourth anniversary of the widespread protests that erupted across the country after George Floyd's death in Minneapolis. As such, we expect protests and disruptions to continue.
Key Takeaways The importance of the Israel-Palestine conflict in academic and activist circles as well as Jewish and Arab diasporas, the media focus on the crisis, and the polarization surrounding the issue creates an environment conducive to further disruption and ethnically motivated violence. The deepening of political schisms, particularly between Western leftists and Western liberals, will bring to bear significant domestic, foreign, and policy implications. |